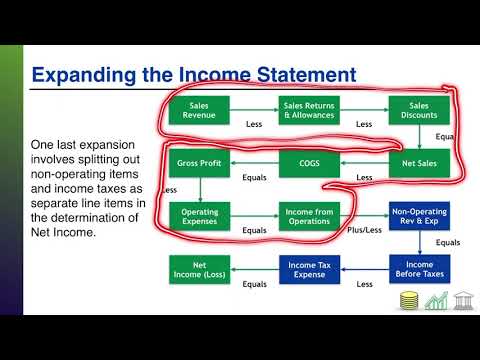
Content

Estimated Base This formula applies to all indirect costs, whether manufacturing overhead, administrative costs, distribution costs, selling costs, or any other indirect cost. To determine whether or not there is a factual relationship between the activity drivers and cost of objects. X & co produces two products E and F which is made from the same material. Till date X and co was using traditional absorption costing to its product. The cost of the maintenance is allocated to the products produced by the machine, when the machine requires periodic maintenance.
MID AMERICA APARTMENT COMMUNITIES INC. Management’s … – Marketscreener.com
MID AMERICA APARTMENT COMMUNITIES INC. Management’s ….
Posted: Tue, 14 Feb 2023 21:19:10 GMT [source]
As the Activity Cost Driver Definition dictionary expands—either to reflect more detail about activities or to expand the scope of the model to the entire enterprise—the demands on the computer programs used to store and process the data escalate. Suppose a company has 150 activities in its enterprise ABC model, applies the costs in these activities to some 600,000 cost objects , and runs the model monthly for two years. That would require data estimates, calculations, and storage for more than 2 billion items. Generally, there are no regulations and standards in any industry that stipulates the selection of a cost driver. The selection of cost drivers is dependent on the expenses variables incurred in the course of the production period. The next step of activity-based costing is to determine resource drivers. The objects that are linked to an activity, that activity consumes resources at a specified rate is called resource drivers.
Overview of Activity Driver
Distributes the resource or activity cost evenly over the targets to which this driver is linked. Denotes a driver based on a quantity of resources or activities that are consumed. This is the only method available if you select a driver category of Duration Drivers, Intensity Drivers, or Transactional Drivers. It helps management see a business’s various departments as one single business unit as these drivers create a relationship between the departments. Can be identified with a product, process, department, or customer and tracked back to why the cost was incurred. It makes that allocation possible, and only then the real cost of the product being manufactured will be determined.
- Traditionally, in a job order cost system and process cost system, overhead is allocated to a job or function based on direct labor hours, machine hours, or direct labor dollars.
- The costs required for producing the true product is obtained by breaking all the costs involved in its manufacturing.
- The number of labor hours has a direct impact on the electric bill.
- And in the long-term, if we understand that certain overheads are influenced by certain things, it gives us the ability to hopefully control our costs in these areas as well.
- Identify the activities that consume resources and assign costs to those activities.
In the case of our https://personal-accounting.org/ service department, the traditional ABC survey produced a work distribution of 70%, 10%, and 20% of the employees’ time performing the department’s three activities. A per unit cost is calculated by dividing the total dollars in each activity cost pool by the number of units of the activity cost drivers. As an example to calculate the per unit cost for the purchasing department, the total costs of the purchasing department are divided by the number of purchase orders. Once the per unit costs are all calculated, they are added together, and the total cost per unit is multiplied by the number of units to assign the overhead costs to the units. Look at the overhead rates computed for the four activities in the table below.
How ABC Works in Practice
Activity cost drivers include direct labor hours, the cost of warehousing, order frequency, and product returns. When a factory machine requires periodic maintenance, the cost of the maintenance is allocated to the products produced by the machine. After every 1,000 machine hours, there is a maintenance expense of $500. Therefore, every machine hour results in a 50-cent (500 / 1,000) maintenance cost allocated to the product being manufactured based on the cost driver of machine hours. Typical examples of this would be things like factory rent rates, supervisors’ salaries, and also costs to do with things like procuring materials, setting up equipment etc. All of these things are indirect costs that can’t be directly related to products being produced.
Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts.
Accounting Topics
After you get the figures, you would be able to see how your cost per unit has changed with changes in your production strategies. You measure the number of items produced or delivered and then divide it by total cost. This method allows you to identify the current costs per unit for various products, services, and customers . The Activity Based Costing approach relates indirect cost to the activities that drive them to be incurred.
What is ABC cost driver?
An activity cost driver refers to actions that cause variable costs to increase or decrease for a business. Therefore, identifying what product/service is causing particular costs can help the business to become more profitable by better understanding the specific activities that are driving the costs.
In addition, consider whether or not the cost driver activity is easily measurable. It is also necessary to consider the cost behavior of the relevant cost. The relevant cost refers to the cost’s response to the activity of the driver. In addition, approximate the relationship between costs and cost drivers using regression analysis. Manufacturing businesses with high overhead costs use activity-based costing to get a clearer picture of where money is going.
The classical scenario we see here is trying to work out the cost of producing products. The below is just a very small snippet from our P2 course, which is taught by 2020 lecturer of the year nominee Nick Drape. A former practicing accountant and Kaplan Financial teacher, Nick currently lectures at the University of Liverpool where he specialises in management accounting and financial management. You can access the entire P2 course along with all of our other objective test and case study courses by purchasing our All Access membership.
- An activity cost driver is an action that triggers higher or lower variable costs for a business.
- Such activity drivers may include machines, materials, labor, and so on.
- For example, management estimated the company would purchase 100,000 pieces of materials that would require overhead costs of $200,000 for the year.
- Generally, when working with activity driver analysis, there must be an activity happening.
- For example, an indirect or variable cost may be relevant at the unit level, the batch level, the product level, the customer level, or the facility level.
- Activity-based costing is a costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to related products and services.
